Disconnected Registry/Mirroring
I've been through this process a lot in my time at Red Hat but there have been some recent changes to the mirror-registry tooling that I want to capture. I use my blog posts for two parts. One is to document processes I repeat more than one time. Secondly, if it works, it is worth sharing.
For the artifacts used during this blog, go to:

VM/Host Requirements

I'm restricting this install to only X86_64 and a specific 4.18 release (4.18.13).
This is all coming from the downloads page on console.redhat.com
The direct link to the OC binary (if you don't already have), the OC-mirror binary, and the mirror-registry.tar file are below. This is assuming the Quay registry is running on RHEL 9.
https://mirror.openshift.com/pub/cgw/mirror-registry/latest/mirror-registry-amd64.tar.gz
https://mirror.openshift.com/pub/openshift-v4/x86_64/clients/ocp/latest/oc-mirror.rhel9.tar.gz
Mirroring Process
After downloading these, let's go through the following steps.
- Install podman and openssl
dnf install -y podman
dns install -y openssl- I like to allocate most of my space to the /home partition when building my server. This makes things easier in my opinion.
cp mirror-registry.amd64.tar.gz /home
cd /home
tar xvzpf mirror-registry.amd64.tar.gz
Now the oc binary and the oc-mirror binary
tar xvzpf oc-mirror.tar.gz
tar xvzpf openshift-client-linux-amd64-rhel9.tar.gz
cp kubectl oc oc-mirror /usr/local/bin
chmod 755 /usr/local/bin/oc
chmod 755 /usr/local/bin/oc-mirror
chmod 755 /usr/local/bin/kubectl- Untar the contents of the mirror-registry file.
tar xvzpf mirror-registry-amd64.tar.gzThis will extract the following 4 files:
image-archive.tar
execution-environment.tar
mirror-registry
sqlite3.tar
- From /home, run the following:
cd /home
mkdir mirror
./mirror-registry install --quayHostname <full-fqdn-of-this-host> --quayRoot /home/mirrorThis will result in an Ansible playbook running as follows
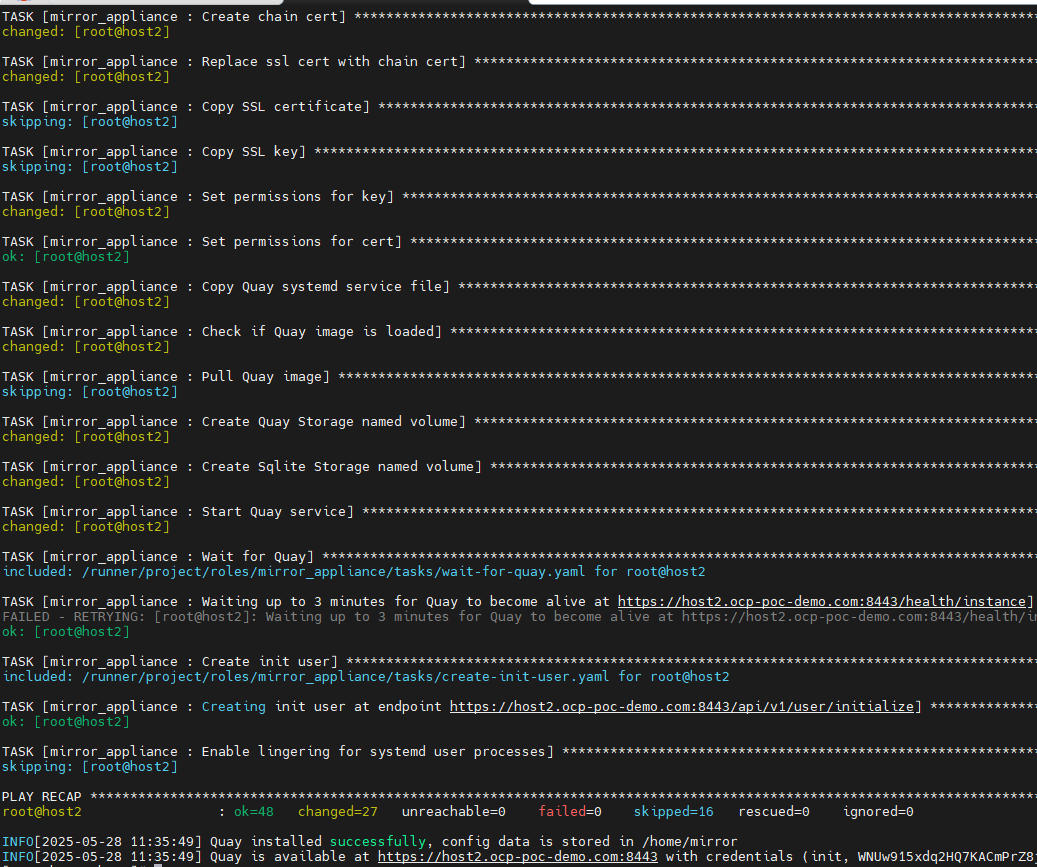
At the end of this output, credentials for the init user will be provided. Take note of the username and password. I like to create a file called quay-creds in /home/mirror directory.
- Let's open up port 8443 and trust the root certificate of Quay registry.
cp /home/mirror/quay-rootCA/rootCA.pem /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/
update-ca-trust extract
firewall-cmd --add-port=8443/tcp --permanent
firewall-cmd --reload
- Occasionally, I've run into issues with the partition that containers /var/containers filling up during this process. To fix this, you could either build the server with around 100GB of space for /var/lib/containers or edit the storage.conf file to put the container storage somewhere else. I picked the latter.
mkdir /home/containers
mkdir /home/containers-run
Change /etc/containers/storage.conf as follows:
runroot = "/home/containers-run/storage"
graphroot = "/home/containers/storage"
A sample of the file I have is on the Git repo and called storage.conf
Restart podman service after making this change.
systemctl restart podman- Grab your pull secret from:
Save this file as pull-secret
Convert this to json format (dnf install jq if you need to)
cat ./pull-secret | jq . > pull-secret.jsonConvert your init username and password to base64 with a command similar to follows:
echo -n 'init:<yourinitpassword>'|base64 -w0Add this to the top of your pull-secret.json file you made earlier. Make a backup of this in case it gets messed up.
The final version should start like this:
{
"auths": {
"host2.ocp-poc-demo.com:8443": {
"auth": "<yourbase64encodedinitusernameandpassword>",
"email": "me@whereever.com"
},
"cloud.openshift.com": {
"auth": - If you running as root, make a directory to house your docker creds.
mkdir /root/.docker
cp pull-secret.json /root/docker/config.jsonYou may also need to login to your Quay registry one-time just to be on the safe-side.
podman login <yourquayfqdn>:8443- Next, we will mirror the 4.18 base images. The imageset.conf referenced here is located at:
cd /home
oc-mirror --config imageset.yaml --workspace file://home/base-images-418 docker://<fqdnofyourhost>:8443 --v2You will start to see output like below:
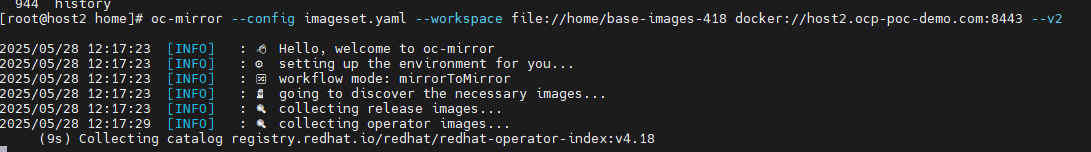
At the end, you will see output similar to the following:
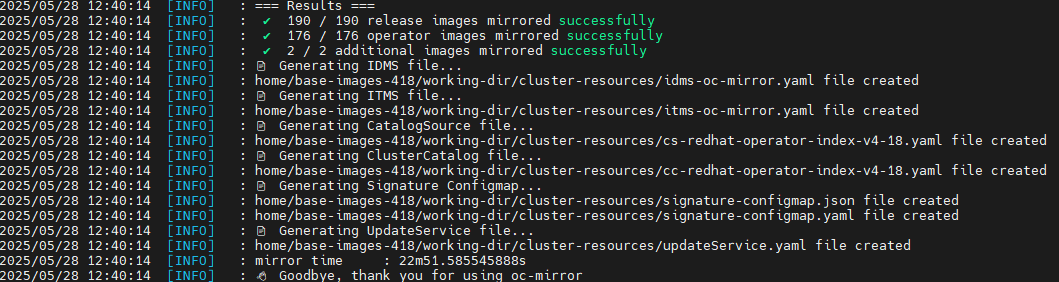
It took about 22 minutes to run in my environment. There were 190 release images and 176 operator images (ACM/Multicluster-Engine).
Installing Cluster Based on this Disconnected Registry
For this part of the install, I will use an on-premise based agent-install.
- Create the install-config.yaml. Here is a sample for a compact/3-node cluster.
apiVersion: v1
baseDomain: ocp-poc-demo.com
compute:
- architecture: amd64
hyperthreading: Enabled
name: worker
replicas: 0
controlPlane:
architecture: amd64
hyperthreading: Enabled
name: master
replicas: 3
metadata:
name: disconnected
networking:
clusterNetwork:
- cidr: 10.128.0.0/14
hostPrefix: 23
machineNetwork:
- cidr: 192.168.4.0/24
networkType: OVNKubernetes
serviceNetwork:
- 172.30.0.0/16
platform:
baremetal:
apiVIP: "192.168.4.60"
ingressVIP: "192.168.4.61"
pullSecret: '{"auths":{"host2.ocp-poc-demo.com:8443":{"auth":"aW5pdDpPztrFNTRoMEM3b0g5WnUxR3Y4RtNJVldVTnpENlh5QQ=="}}}'
sshKey: 'ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABgQDY4FFXOr3y52gyDVGeZvtf+Le3NLkllsGqJfKLWQOpHpL7AFlibK/YBlZMD5yT//ZVJ1g+AreSZpcbngvcVFdMhSL8eFSHGDAT1aZIRVdPnQ/3eNrLsLjldiR+HT191QEHl3DHY0ZyT37rl30CQ5xiUd7/5ZemiArypnxjelsaYIEnT5UcRDOAk3CDPbF8M0gNNwNAqKmRGNKcJmTgSSLjJGDblxNGMk5TIl21yxNZqJqDdQgj4s9cp0OM5ZPg1ZE9syKSqg/PkNcOZ5PVzFrOpVsVJTiSnTPlU5bmqbrwnH3ij2QdtSBh4fznchaY6z38uT8EBzXycuvaILLVVl2Qa/mITjujMVicnDYpilUeoDnd6/ZR6QZfKnCBz/T4MQ24wC2TlxXqtNSpaIbAOsNovbOvDmt5iDD1gsRGXfyrLjDAzUJKHOKWGkLbcolGjSemqzvfeDU/7iA90zUhGORmbawQcQeRHEwzIXzpL+Sby3ntrx4a/KI5STw9rCTAsPE= keith@host3.ocp-poc-demo.com'
additionalTrustBundle: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIDcTCCAlmgAwIBAgIUDOyG3KLLwQsVkSahzbuaHFEZxU4wDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEL
BQAweTELMAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxCzAJBgNVBAgMAlZBMREwDwYDVQQHDAhOZXcgWW9y
azENMAsGA1UECgwEUXVheTERMA8GA1UECwwIRGl2aXNpb24xKDAmBgNVBAMMH3Rl
c3R2bS1kbnZyLnZvaXAuY2hhcnRlcmxhYi5jb20wHhcNMjUwNTE2MjAyNzEyWhcN
MjYwNTA3MjAyNzEyWjAaMRgwFgYDVQQDDA9xdWF5LWVudGVycHJpc2UwggEiMA0G
CSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4IBDwAwggEKAoIBAQDN0HPGI7rR6DuvcfFzOzA45AHjoKDY
kfiSCRzVRtm8SwA3ckORMkaGtTcPne9xPBoWZGBSBwRIzc2sLuwaMVs7cqavSHeo
x8jYdUG1esnSdyfAOvLN/+gjvH9f6b6S6fCE+RWoI0YoMg8CNV3kOLOh46XDHWuM
eVSz2n2b5Ni/zufZO6S9ht/QR0VBn4J0DSnrRtc4jvi/1AM8+YFRF7e1n0jqTGyv
u/cXn9kisbvH9ouZ/0weX7uz4E00VLRiX4a5RZlpNzSlwb6BRINh2HwE1bCUx35p
QWhZpiE7A9xMlHs6jfXHTMIRW9+AgxXL6PzBubqWIngk5U7+8yU+n5avAgMBAAGj
UDBOMAsGA1UdDwQEAwIC5DATBgNVHSUEDDAKBggrBgEFBQcDATAqBgNVHREEIzAh
gh90ZXN0dm0tZG52ci52b2lwLmNoYXJ0ZXJsYWIuY29tMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUA
A4IBAQAT/WKxvtn59MnaO7nz+kfWrekPmr8W0vJiC04b3goWfnhdjGW/NXCuutio
K8ESyazUfTaWYLHkbq/Yx+A3I/7T5aA9rFPkXhIE4KRWGmFciMXPfmKvCBhsLhrx
toL7WD5dthrLJbeRlzaG0zXwf2IAa3pzx72SBdBh81cW6UY88O6DwlIVN66tMpIk
P2FWUoZ22pHCKMkNSh8y1xfL3ddP0OhlcsobS000E4vgXxeGrFEKkyuYpP8TsPzZ
SdlJwXWIl3vhpmLdFiNXd5Td81/UYbh62t/A9ZzS1lY55cGY7C6BvN32RUjkM2Z/
BCmhQXTqg5ar6O/nct2VXKIuvtMl
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIID5DCCAsygAwIBAgIUMy2WGoXqDOQbrKb8it7Vyi7D0iMwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEL
BQAweTELMAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxCzAJBgNVBAgMAlZBMREwDwYDVQQHDAhOZXcgWW9y
azENMAsGA1UECgwEUXVheTERMA8GA1UECwwIRGl2aXNpb24xKDAmBgNVBAMMH3Rl
c3R2bS1kbnZyLnZvaXAuY2hhcnRlcmxhYi5jb20wHhcNMjUwNTE2MjAyNzEwWhcN
MjgwMzA1MjAyNzEwWjB5MQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzELMAkGA1UECAwCVkExETAPBgNV
BAcMCE5ldyBZb3JrMQ0wCwYDVQQKDARRdWF5MREwDwYDVQQLDAhEaXZpc2lvbjEo
MCYGA1UEAwwfdGVzdHZtLWRudnIudm9pcC5jaGFydGVybGFiLmNvbTCCASIwDQYJ
KoZIhvcNAQEBBQADggEPADCCAQoCggEBAKSWa+ySDNORb7UprChr1nT8WxcEdyK6
gkvwZ2TBhU/rqDqZLMqyIvtFn57xgHpOhseyCnOVAN7BRJDx09xZR9o/O9oqFu2B
sZgcTEI8Rc3/gH8AnTaXVISr1XXOwDiS7ILRlaT+TsCVim59qJ1H1KNEk5kDROJr
Ol/1wx7cnNcKFQgwKzf6LgfLYcAdOxLMvl9CBVxSATpvyf2C6CnimhaNYDbpXmKp
PLaWIvRwpnd4ZsjpVbECH6s9K8MAQ47YGvkbnVlDOYStUUA4qhoXuxueFZk/Sp+K
ugR0uNtdaf79u0Kd0yInTMrAOQPpUKNJ2LX/fdGH6xA3TDnNpQgcL/sCAwEAAaNk
MGIwCwYDVR0PBAQDAgLkMBMGA1UdJQQMMAoGCCsGAQUFBwMBMCoGA1UdEQQjMCGC
H3Rlc3R2bS1kbnZyLnZvaXAuY2hhcnRlcmxhYi5jb20wEgYDVR0TAQH/BAgwBgEB
/wIBATANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFAAOCAQEAKkUirlO+agjwL1c4DOv/ulYu6CdQQ4tM
+sK2cftREQsLG+85++8/hXOmUmuWmR+NfOVLSumwJXw8Hn4/HK7oBU3uQdIOsEYl
tcUH9tcGXfHvnnGKSTmCTVpZ99wvWMfvpLvnBu5G6x/bXQ3KUza7GdjpVorI3RHW
K9hVL/buFgplU5reJRXndxXRw0+Q2O5dNn0UsClUklrabDlEBPjiXKYeoiTdRfMl
x7pU+hO0L9JYdcN6XfGSB/CbXhugXajPaYAf8wcqSCEZWzsL14cBznKRDbYfk2sZ
8m2IwgGdLbR9dBjxaquNVWm/0daqMIG4+paN0RLJKhY0jxt88BKKqQ==
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
imageDigestSources:
- mirrors:
- host2.ocp-poc-demo.com:8443/openshift/release
source: quay.io/openshift-release-dev/ocp-v4.0-art-dev
- mirrors:
- host2.ocp-poc-demo.com:8443/openshift/release-images
source: quay.io/openshift-release-dev/ocp-release
Some notes:
The imageDigestSources/mirrors section maps the source quay.io release images to the location they are stored on your Quay registry. Change the host2.ocp-poc-demo.com to the location where openshift/release and openshift-release-dev/ocp-release exist on your Quay registry.
The certificates need to be indented (2 spaces from additionalTrustBundle) and this will contain your the chain for the signer and quay registry cert. It is self-signed by default.
pull-secret and SSH key should be one long line. The pull-secret is just the pull-secret for your disconnected registry.
The full example is located at:
https://github.com/kcalliga/disconnected_registry/blob/main/agent-install/install-config.yaml
- For the agent-config.yaml, just add your three nodes like the following example:
apiVersion: v1beta1
kind: AgentConfig
metadata:
name: cluster-agent-config
rendezvousIP: 192.168.4.200
hosts:
- hostname: host1
interfaces:
- name: eth0
macAddress: 52:54:00:bc:e6:73
networkConfig:
interfaces:
- name: eth0
type: ethernet
state: up
mtu: 1500
ipv4:
enabled: true
dhcp: false
address:
- ip: 192.168.4.200
prefix-length: 24
ipv6:
enabled: false
dhcp: false
autoconf: false
dns-resolver:
config:
search:
- disconnected.ocp-poc-demo.com
server:
- 8.8.8.8
- 8.8.4.4
routes:
config:
- destination: 0.0.0.0/0
next-hop-address: 192.168.4.1
next-hop-interface: eth0
table-id: 254
- hostname: host3
interfaces:
- name: eth0
macAddress: 52:54:00:6d:62:9b
networkConfig:
interfaces:
- name: eth0
type: ethernet
state: up
mtu: 1500
ipv4:
enabled: true
dhcp: false
address:
- ip: 192.168.4.202
prefix-length: 24
ipv6:
enabled: false
dhcp: false
autoconf: false
dns-resolver:
config:
search:
- disconnected.ocp-poc-demo.com
server:
- 8.8.8.8
- 8.8.4.4
routes:
config:
- destination: 0.0.0.0/0
next-hop-address: 192.168.4.1
next-hop-interface: eth0
table-id: 254
- hostname: host6
interfaces:
- name: eth0
macAddress: 52:54:00:18:10:5b
networkConfig:
interfaces:
- name: eth0
type: ethernet
state: up
mtu: 1500
ipv4:
enabled: true
dhcp: false
address:
- ip: 192.168.4.206
prefix-length: 24
ipv6:
enabled: false
dhcp: false
autoconf: false
dns-resolver:
config:
search:
- disconnected.ocp-poc-demo.com
server:
- 8.8.8.8
- 8.8.4.4
routes:
config:
- destination: 0.0.0.0/0
next-hop-address: 192.168.4.1
next-hop-interface: eth0
table-id: 254Notes:
These contain 3 hosts/nodes in my environment. I need to add an element for each node that defines its mac-address, ip-address, gateway, etc.
Rendezvous can be picked automatically by the installer or you can specify. This is one of the IP addresses associated with the cluster that will be used for the agent to run. After the other nodes are built, this will pivot to be another control-plane/worker node.
- After creating/editing these two files, make a directory for them. I typically put this in in a directory called install. Before you run the openshift-install binary be sure to back this up or just copy them to the install directory but keep a copy somewhere else as shown below.
mkdir ./install
cp install-config.yaml agent-config.yaml- Download the openshift-install binary if you do not already have it.
The current link is here:
- Untar the openshift-install binary and copy to /usr/local/bin
tar xvzpf openshift-install-linux.tar.gz
cp openshift-install /usr/local/bin
chmod 755 /usr/local/bin/openshift-install- Run the following command to create the ISOs needed for install.
openshift-install agent create image --dir ./install- Mount the ISOs on each of the nodes and follow normal install processes.
- During the install, you can run the following openshift-install commands to monitor progress:
openshift-install agent --dir install wait-for bootstrap-complete --log-level=debug
openshift-install agent --dir install wait-for install-complete --log-level=debugDisconnected Operators
For disconnected operators, follow this process:
- Find the operators needed for the cluster you just installed.
oc mirror list operators --catalog registry.redhat.io/redhat/redhat-operator-index:v4.18- After you run this, you see output similar to follows:
NAME DISPLAY NAME DEFAULT CHANNEL
3scale-operator threescale-2.15
advanced-cluster-management release-2.13
amq-broker-rhel8 7.12.x
amq-broker-rhel9 7.13.x
amq-online stable
amq-streams stable
amq-streams-console alpha
amq7-interconnect-operator 1.10.x
ansible-automation-platform-operator stable-2.5
ansible-cloud-addons-operator stable-2.5-cluster-scoped
apicast-operator threescale-2.15
apicurio-registry-3 3.x
authorino-operator stable
aws-efs-csi-driver-operator stable
aws-load-balancer-operator stable-v1
bamoe-businessautomation-operator 8.x-stable
bamoe-kogito-operator 8.x
bpfman-operator latest
businessautomation-operator stable
cephcsi-operator stable-4.18
cincinnati-operator v1
cli-manager tech-preview
cluster-kube-descheduler-operator stable
cluster-logging stable-6.2
cluster-observability-operator stable
clusterresourceoverride stable
compliance-operator stable
container-security-operator stable-3.14
costmanagement-metrics-operator stable
cryostat-operator stable
datagrid stable
devspaces stable
devworkspace-operator fast
dns-operator stable
dpu-network-operator stable
dpu-operator stable
eap stable
elasticsearch-operator stable-5.8
external-dns-operator stable-v1
fence-agents-remediation stable
file-integrity-operator stable
fuse-apicurito fuse-apicurito-7.13.x
fuse-console 7.13.x
fuse-online latest
gatekeeper-operator-product stable
gcp-filestore-csi-driver-operator stable
ingress-node-firewall stable
jaeger-product stable
jws-operator alpha
kernel-module-management stable
kernel-module-management-hub stable
kiali-ossm stable
kubernetes-nmstate-operator stable
kubevirt-hyperconverged stable
kueue-operator stable-v0.1
lifecycle-agent stable
lightspeed-operator alpha
limitador-operator stable
local-storage-operator stable
logic-operator-rhel8 alpha
loki-operator stable-6.2
lvms-operator stable-4.18
machine-deletion-remediation stable
mcg-operator stable-4.18
metallb-operator stable
mta-operator stable-v7.3
mtc-operator release-v1.8
mtr-operator alpha
mtv-operator release-v2.8
multiarch-tuning-operator stable
multicluster-engine stable-2.8
multicluster-global-hub-operator-rh release-1.4
nbde-tang-server stable
netobserv-operator stable
nfd stable
node-healthcheck-operator stable
node-maintenance-operator stable
node-observability-operator alpha
numaresources-operator 4.18
ocs-client-operator stable-4.18
ocs-operator stable-4.18
odf-csi-addons-operator stable-4.18
odf-dependencies stable-4.18
odf-multicluster-orchestrator stable-4.18
odf-operator stable-4.18
odf-prometheus-operator stable-4.18
odr-cluster-operator stable-4.18
odr-hub-operator stable-4.18
openshift-builds-operator latest
openshift-cert-manager-operator stable-v1
openshift-custom-metrics-autoscaler-operator stable
openshift-gitops-operator latest
openshift-pipelines-operator-rh latest
openshift-secondary-scheduler-operator stable
openstack-operator stable-v1.0
opentelemetry-product stable
orchestrator-operator stable
pf-status-relay-operator stable
power-monitoring-operator tech-preview
ptp-operator stable
quay-bridge-operator stable-3.14
quay-operator stable-3.14
recipe stable-4.18
red-hat-camel-k 1.10.x
red-hat-hawtio-operator stable-v1
redhat-oadp-operator stable-1.4
rh-service-binding-operator stable
rhacs-operator stable
rhbk-operator stable-v26.2
rhcl-operator stable
rhdh fast
rhods-operator stable
rhpam-kogito-operator 7.x
rhsso-operator stable
rhtas-operator stable
rook-ceph-operator stable-4.18
run-once-duration-override-operator stable
sandboxed-containers-operator stable
secrets-store-csi-driver-operator stable
security-profiles-operator release-alpha-rhel-8
self-node-remediation stable
serverless-operator stable
service-registry-operator 2.x
service-telemetry-operator stable-1.5
servicemeshoperator stable
servicemeshoperator3 stable
skupper-operator stable-2
smart-gateway-operator stable-1.5
smb-csi-driver-operator stable
sriov-network-operator stable
submariner stable-0.20
tang-operator alpha
tempo-product stable
topology-aware-lifecycle-manager stable
trustee-operator stable
vertical-pod-autoscaler stable
volsync-product stable
watcher-operator stable-v1.0
web-terminal fast
windows-machine-config-operator stable
- Grab the specific operators that will be needed by this disconnected cluster now and form a new imageset. This will be called imageset-operators.yaml
kind: ImageSetConfiguration
apiVersion: mirror.openshift.io/v2alpha1
mirror:
operators:
- catalog: registry.redhat.io/redhat/redhat-operator-index:v4.18
packages:
- name: advanced-cluster-management
- name: multicluster-engine
- name: ocs-client-operator
- name: ocs-operator
- name: odf-csi-addons-operator
- name: odf-dependencies
- name: odf-operator
- name: kubevirt-hyperconverged
- name: local-storage-operator
additionalImages:
- name: registry.redhat.io/ubi8/ubi:latest
- name: quay.io/openshifttest/hello-openshift@sha256:4200f438cf2e9446f6bcff9d67ceea1f69ed07a2f83363b7fb52529f7ddd8a83advanced-cluster-management and multicluster-engine were already installed but we are installing the following as well:
Openshift Virtualization which is listed as kubevirt-hyperconverged
Openshift Data Foundation which is comprised of ocs-operator, ocs-operator, odf-cs-addons-operator, odf-dependencies, odf-operator
local-storage-operator allows local disks to be discovered in order to become part of Openshift Data Foundation/Ceph storage.
- Run the following to get these:
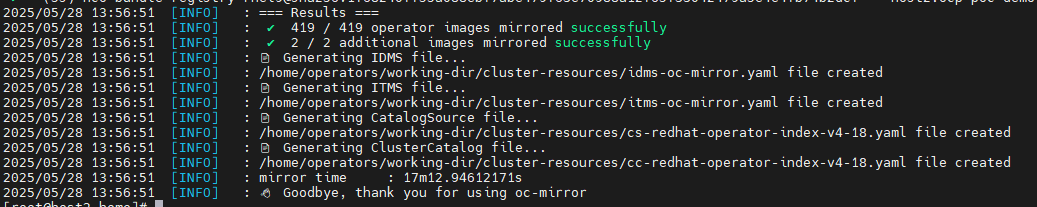
oc-mirror --config imageset-operators.yaml --workspace file:///home/operators docker://host2.ocp-poc-demo.com:8443 --v2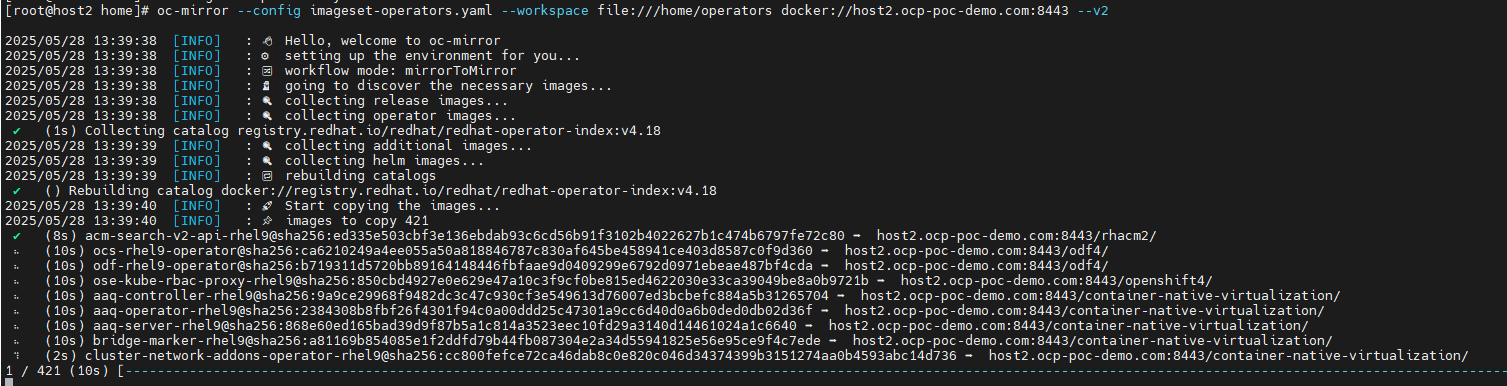
This took about 17 minutes to run
Using Disconnected Operators on Cluster
To use operators in a disconnected manner, do the following:
- Disable the defaultsources.
oc patch OperatorHub cluster --type json -p '[{"op": "add", "path": "/spec/disableAllDefaultSources", "value": true}]'- Add new catalogsource
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: CatalogSource
metadata:
name: my-operator-catalog
namespace: openshift-marketplace
spec:
sourceType: grpc
grpcPodConfig:
securityContextConfig: legacy
image: host2.ocp-poc-demo.com:8443/redhat/redhat-operator-index:v4.18
updateStrategy:
registryPoll:
interval: 30moc apply -f catalogsource.yaml- Add new imagecontentsourcepolicy
apiVersion: operator.openshift.io/v1alpha1
kind: ImageContentSourcePolicy
metadata:
labels:
operators.openshift.org/catalog: "true"
name: operator-0
spec:
repositoryDigestMirrors:
- mirrors:
- host2.ocp-poc-demo.com:8443/container-native-virtualization
source: registry.redhat.io/container-native-virtualization
- mirrors:
- host2.ocp-poc-demo.com:8443/odf4
source: registry.redhat.io/odf4oc apply -f imagecontentsourcepolicy.yamlYou should now be able to pull the operator images from OperatorHub in your disconnected environment.




